v3.x
Introduction
ColdBox ORM Module
The cborm module is a module that will enhance your experience when working with the ColdFusion ORM powered by Hibernate. It will not only enhance it with dynamic goodness but give you a fluent and human approach to working with Hibernate. Basically making working with Hibernate not SUCK!

Some Features
Service Layers with all the methods you could probably think off to help you get started in any project
Virtual service layers so you can create virtual services for any entity in your application
Automatic RESTFul resources handler, focus on your domain objects and business logic, not the boilerplate of REST
ActiveEntityour implementation of Active Record for ORMFluent queries via Hibernate's criteria and detached criteria queries with some Dynamic CFML goodness
Automatic transaction demarcation for save and delete operations
Dynamic finders and counters for expressive and fluent shorthand SQL
Automatic Java casting
Entity population from json, structs, xml, and queryies including building up their relationships
Entity validation via cbValidation
Includes the Mementifier project to produce memento states from any entity, great for producing JSON
Ability for finders and queries to be returned as Java streams using our cbStreams project.
In other words, it makes using an ORM not SUCK!
Versioning
The ColdBox ORM Module is maintained under the Semantic Versioning guidelines as much as possible.Releases will be numbered with the following format:
And constructed with the following guidelines:
Breaking backward compatibility bumps the major (and resets the minor and patch)
New additions without breaking backward compatibility bumps the minor (and resets the patch)
Bug fixes and misc changes bumps the patch
License
Apache 2 License: http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Important Links
ForgeBox: https://forgebox.io/view/cborm
Discussion & Help

The Ortus Community is the way to get any type of help for our entire platform and modules: https://community.ortussolutions.com
Professional Open Source

The ColdBox ORM Module is a professional open source software backed by Ortus Solutions, Corp offering services like:
Custom Development
Professional Support & Mentoring
Training
Server Tuning
Security Hardening
Code Reviews
HONOR GOES TO GOD ABOVE ALL
Because of His grace, this project exists. If you don't like this, then don't read it, it's not for you.
"Therefore being justified by faith, we have peace with God through our Lord Jesus Christ: By whom also we have access by faith into this grace wherein we stand, and rejoice in hope of the glory of God." Romans 5:5
Intro
Release History
In this section you will find the release notes for each version we release under this major version. If you are looking for the release notes of previous major versions use the version switcher at the top left of this documentation book. Here is a breakdown of our major version releases.
Version 2.0
A complete rewrite of the module to support a more modern and fluent approach to working with Hibernate/ColdFusion ORM. In this release we had to support 3 versions of Hibernate: 3 (Lucee), 4 (ACF 2016) and 5 (ACF 2018), which in itself proved to be a gargantuan task.
We also focused on bringing more functional programming aspects to working with collections of entities and even introduced cbStreams as part of the cborm module. This gives you the ability to produce streams out of any method that produces a collection of entities.
We also focused on converting the state of an object graph to a raw ColdFusion data struct as we live in the world of APIs. We include the mementifier module which allows every single entity to have a getMemento() method that will convert itself and its relationships to raw CF data constructs so you can take that state and either marshall it to another format (json,xml,excel) or audit the state.
Version 1.0
The first version of the cbORM series that focused on expanding the native ColdFusion ORM methods and exposing much more Hibernate functionality to the CFML world.
What's New With 3.9.0
August 10, 2022
Added
New
when( boolean, success, fail )fluent construct forActiveEntity,VirtualEntityServiceand theBaseORMServiceto allow for fluent chaining of operations on an entity or its service.Migration to new ColdBox Virtual App Testing approaches
Removed unnecessary on load logging to increase performance
Hibernate 5.4 on Lucee experimental testing
Fixed
countWhere()invalid SQL exception if no arguments are provided: #54
What's New With 3.8.0
March 11, 2022
Fixed
CBORM-32 - Non-Primary DSN Entities not found. Multi-datasource discovery of entities using virtual services and active entity. This was a regression since version 1.5. This brings back multi-datasource support for active entity, and virtual entity services. #52
Detached
Subquerieswas marked as asingletonwhen indeed it was indeed atransient. This could have created scoping issues on subquery based detached criteria building.Var scoping issues in
BaseBuilderdetached projectionsDetachedCriteriaBuilderwas not passing thedatasourceto native criteria objects
Added
Root
docker-compose.ymlto startup MySQL, or PostgreSQL in docker, for further hacking and testing.Java proxy caching to avoid Lucee OSGi issues and increase Java object building performance
New method in the
BaseOrmService:buildJavaProxy()which leverages ourJavaProxyBuilderused mostly internally.Lazy loading of SQL Helper in criteria queries
New module template guidelines and CI
Leverage WireBox aliases for construction of internal objects
Tons of internal docs and links to hibernate docs
What's New With 3.7.0
January 13, 2022
What's New With 3.6.0
January 10, 2022
What's New With 3.5.0
December 16, 2021
Fixed
CBORM-20 ActiveEntity evict() had the wrong method and arguments delegated to the parent class.
CBORM-9 ACF2021 - org.hibernate.SessionFactory.getAllClassMetadata is no longer supported
Improved
CBORM-14 Inline datasource discovery in base orm service to get a performance boost
CBORM-13 virtual entity service double creating the orm utility, use the parent one instead of duplicating the effort
CBORM-12 Lazy load the getORMUtil() and use it only when required.
Added
CBORM-22 New orm util support method: setupHibernateLogging() thanks to michael born
CBORM-19 Added a isInTransaction() util helper method to all the orm services.
CBORM-18 New ORM events based on Hibernate 5.4 Events: ORMFlush, ORMAutoFlush, ORMPreFlush, ORMDirtyCheck, ORMEvict, and ORMClear
CBORM-17 Hibernate 5.4 support for lucee new extension
CBORM-16 Adobe 2021 support and testing automations
CBORM-15 Migration to github actions
CBORM-11 Allow Criteria Builder Get() and getOrFail() Methods to Return Projection List Properties
CBORM-21 New cfformating rules
Compatibility
If you upgrade your lucee ORM extension to use Hibernate 5.4, all positional paramters in HQL using
?has been deprecated. You will have to use the?xapproach wherexis a number according to the position in the sql:
What's New With 3.3.0
April 27, 2021
Added
New
eventPrefixsetting so you can prefix the resource REST CRUD events with whatever you like.Useful exceptions when
resultsstruct does not have the required keysAbility to override the name of the method to use for persistence on the ORM services. Using the
variables.saveMethodproperty or thesavemethodargument.Ability to override the name of the method to use for deleting entities on the ORM services. Using the
variables.deleteMethodproperty or thedeleteMethodargument.cbSwagger docs added to the base resource handler
Changed
Added ACF2016 compatibilities on elvis operator which sucks on ACF2016
Avoid using member function son some arrays to allow for working with Java arrays
What's New With 3.2.x
March 31, 2021
Added
Exposed a
getSQLHelper()from criterias to allow for usage of formmatting of sqlNew interception points:
beforeOrmExecuteQuery, afterOrmExecuteQueryfrom the base orm service:executeQuery()method
Fixed
Moved
afterCriteriaBuilderListevent before results conversions
[v3.2.1] => 2021-MAR-31
Fixed
Wrong object to get the event handler manager when doing execute query calls
What's New With 3.1.0
March 30, 2021
What's New With 3.0.0
February 12, 2021
Compatibility Updates
In this major release we have two issues that are not backward compatible:
asQuery now false
asQuery now falseAll properties and arguments that received the asQuery argument are now defaulted to false. Meaning arrays of objects/structs is now the default instead of query objects. If you want to go back to queries, then make sure you add the asQuery : true to the method calls.
cbValidation => cbi18n v2 Upgrade
Our supporting modules have been also upgraded to their major versions mostly to support cbi18n v2. https://coldbox-i18n.ortusbooks.com/intro/release-history/whats-new-with-2.0.0
If you are using localization features with cborm then you must read the compat guide for cbi18n v2.
Release Notes
Bugs
[CBORM-2] -
isDirty()not working withActiveEntitydue to missing entity passed
New Features
[CBORM-3] - Updated
cbValidationto v3 to support cbi18n v2[CBORM-4] -
asQueryupdate to default it to false[CBORM-5] - Document v3 variant in the docs
Improvements
[CBORM-6] - Source code cleanups by applying formatting rules
About This Book
The source code for this book is hosted in GitHub: https://github.com/ortus-docs/cbox-cborm-docs. You can freely contribute to it and submit pull requests. The contents of this book is copyright by Ortus Solutions, Corp and cannot be altered or reproduced without author's consent. All content is provided "As-Is" and can be freely distributed.
The majority of code examples in this book are done in
cfscript.The majority of code generation and running of examples are done via CommandBox: The ColdFusion (CFML) CLI, Package Manager, REPL - https://www.ortussolutions.com/products/commandbox
External Trademarks & Copyrights
Flash, Flex, ColdFusion, and Adobe are registered trademarks and copyrights of Adobe Systems, Inc.
ColdBox, CommandBox, FORGEBOX, TestBox, ContentBox, Ortus Solutions are all trademarks and copyrights of Ortus Solutions, Corp.
Notice of Liability
The information in this book is distributed “as is”, without warranty. The author and Ortus Solutions, Corp shall not have any liability to any person or entity with respect to loss or damage caused or alleged to be caused directly or indirectly by the content of this training book, software and resources described in it.
Contributing
We highly encourage contribution to this book and our open source software. The source code for this book can be found in our GitHub repository where you can submit pull requests.
Charitable Proceeds
10% of the proceeds of this book will go to charity to support orphaned kids in El Salvador - https://www.harvesting.org/. So please donate and purchase the printed version of this book, every book sold can help a child for almost 2 months.
Shalom Children's Home

Shalom Children’s Home is one of the ministries that is dear to our hearts located in El Salvador. During the 12 year civil war that ended in 1990, many children were left orphaned or abandoned by parents who fled El Salvador. The Benners saw the need to help these children and received 13 children in 1982. Little by little, more children came on their own, churches and the government brought children to them for care, and the Shalom Children’s Home was founded.
Shalom now cares for over 80 children in El Salvador, from newborns to 18 years old. They receive shelter, clothing, food, medical care, education and life skills training in a Christian environment. The home is supported by a child sponsorship program.
We have personally supported Shalom for over 6 years now; it is a place of blessing for many children in El Salvador that either have no families or have been abandoned. This is good earth to seed and plant.
Author
Luis Fernando Majano Lainez

Luis Majano is a Computer Engineer with over 15 years of software development and systems architecture experience. He was born in San Salvador, El Salvador in the late 70’s, during a period of economical instability and civil war. He lived in El Salvador until 1995 and then moved to Miami, Florida where he completed his Bachelors of Science in Computer Engineering at Florida International University
He is the CEO of Ortus Solutions, a consulting firm specializing in web development, ColdFusion (CFML), Java development and all open source professional services under the ColdBox, CommandBox and ContentBox stack. He is the creator of ColdBox, ContentBox, WireBox, MockBox, LogBox and anything “BOX”, and contributes to many open source projects. You can read his blog at www.luismajano.com
Luis has a passion for Jesus, tennis, golf, volleyball and anything electronic. Random Author Facts:
He played volleyball in the Salvadorean National Team at the tender age of 17
The Lord of the Rings and The Hobbit is something he reads every 5 years. (Geek!)
His first ever computer was a Texas Instrument TI-86 that his parents gave him in 1986. After some time digesting his very first BASIC book, he had written his own tic-tac-toe game at the age of 9. (Extra geek!)
He has a geek love for circuits, micro-controllers and overall embedded systems.
He has of late (during old age) become a fan of organic gardening.
Keep Jesus number one in your life and in your heart. I did and it changed my life from desolation, defeat and failure to an abundant life full of love, thankfulness, joy and overwhelming peace. As this world breathes failure and fear upon any life, Jesus brings power, love and a sound mind to everybody!
“Trust in the LORD with all your heart, and do not lean on your own understanding.” Proverbs 3:5
Contributors
Will de Bruin
Brad Wood
Getting Started
Overview
The cborm module will enhance your ORM Entities and ColdBox application by providing you with features in the following areas:
Active Record Pattern
You can extend your entities from our
ActiveEntityclass and take advantage of both Active Record and Hibernate ORM
Entity Population
Easily populate entities from json, structs, xml, queries and build up even the entity relationships from flat data.
Entity Marshalling to raw data types (mementifier)
Easily extract the data from entities and their relationships so you can marshall them to json, xml, etc.
Automatic CRUD Resource Handler
If you extend our
cborm.models.resources.BaseHandlerit will generate the full CRUD for a specific entity based on ColdBox Resources
ORM Events
Easily listen to multiple ORM events via ColdBox Interceptors
Service Layers
Enhance the ability to list, query, find entities, work with native hibernate constructs and more.
Validation
We provide you with a
uniquevalidator to validate against unique columns
Just write your entities and their relationships and we will take care of the rest!

Base ORM Service
Let's begin our adventure with the BaseORMService model. This model can be injected or requested via WireBox and will be used to interact with any entity in our system or with Hibernate directly:
This service object acts as an abstraction layer to the ColdFusion ORM (Hibernate) and can work with any entity in your system as all methods most likely receive the entityName argument. You will be able to do the following category of actions from this service class:
Hibernate Session utility methods
Entity metadata methods
Querying methods
Criteria Queries or fluent SQL
Getters
Finders
Dynamic Finders
Counters
Dynamic Counters
Persistence (save,update,delete) and bulk persistence with transactions
Eviction Methods
Population Methods
This means that you don't need to create a service layer CFC in order to work with ORM entities, you can leverage this abstraction to work with your ORM needs. You can also specifically bind (root) the service to a specific entity, which we lovingly call a VirtualEntityService. This way you don't have to be passing the entity names left and right, the virtual entity service will be constructed with the name and all operations will be done upon that entity.
Example
Once you have access to the injected base ORM service, you can use it in all of its glory.
Important Please check out the latest API Docs for the latest methods and functionality: https://apidocs.ortussolutions.com/#/coldbox-modules/cborm/
What is this asStream() call? What are Streams?
A stream is an abstraction, it’s not a data structure. It’s not a collection where you can store elements. The most important difference between a stream and a structure is that a stream doesn’t hold the data. For example you cannot point to a location in the stream where a certain element exists. You can only specify the functions that operate on that data. A stream is an abstraction of a non-mutable collection of functions applied in some order to the data.
More information can be found here: https://forgebox.io/view/cbstreams
Virtual Services
We also have a virtual service layer that can be mapped to specific entities and create entity driven service layers virtually. Meaning you don't have to be passing any entity names to the API methods to save you precious typing time. This is achieved via the VirtualEntityService model which inherits from the BaseORMService class.
You can achieve this in several manners:
Injection
entityService:{EntityName}
Request via WireBox using the DSL argument of
getInstance()getInstance( dsl = entityService:{EntityName} );
Request via a Base ORM Service
createService()
That's it! You can use it just like the BaseORMService except no more passing the entity name.
Example
Concrete Services
This is where you create your own CFC that inherits from our VirtualEntityService and either adds or overrides methods. The virtual and base services takes you about 90% of the way. With you concrete services, you can complete the functionality to your liking.
All you need to do is inherit from the cborm.models.VirtualEntityService and call the parent class constructor with the available arguments:
entityname- The name of the entity to root this service with (REQUIRED)queryCacheRegion- The name of the query cache region if using caching, defaults to#arguments.entityName#.defaultVSCacheuseQueryCaching- Activate query caching, defaults to falseeventHandling- Activate event handling, defaults to trueuseTransactions- Activate transaction blocks on calls, defaults to truedefaultAsQuery- Return query or array of objects onlist(), executeQuery(), criteriaQuery(),defaults to truedatasource- The datasource name to be used for the rooted entity, if not we use the default datasource
Active Entity
If you want to apply an Active Record and fluent feel to your entities then ActiveEntity is just for you. Just inherit from cborm.models.ActiveEntity and you are on your way to Active Record bliss.
ActiveEntity inherits from the VirtualEntityService class which inherits from the BaseORMService class. So you have the full gamut of usage plus the ability for the active entity to validate itself. It has the isValid() and getValidationResults() methods to help you with the validation of a populated entity.
Example Entity
Example Usage
Automatic ORM Resource Handler
If you are creating RESTful services, you can leverage our new Base ORM Handler that will give you a full CRUD service for your entities. All you have to do is the following:
Create your entities
Add mementifier data (https://forgebox.io/view/mementifier)
Add validation data (https://forgebox.io/view/cbvalidation)
Register the resource in your application router or module router
resources( "users" )
Create the handler that will manage that resource and extend our base handler, spice up as needed and you are done:
That's it! This handler will now manage ALL the CRUD operations in REST format for your entity including relationships, validations, pagination and data marshalling.
Installation
Leverage CommandBox to install into your ColdBox app:
System Requirements
Lucee 5.x+
ColdFusion 2016+
Application.cfc Setup
Unfortunately, due to the way that ORM is loaded by ColdFusion, if you are using the ORM EventHandler or ActiveEntity or any ColdBox Proxies that require ORM, you must create an Application Mapping in the Application.cfc like this:
WireBox DSL
The module registers a new WireBox DSL called entityservice which can produce virtual or base ORM entity services. Below are the injections you can use:
entityservice- Inject a global ORM serviceentityservice:{entityName}- Inject a Virtual entity service according toentityName
Module Settings
Here are the module settings you can place in your ColdBox.cfc under moduleSettings -> cborm structure:
Validation
We have also integrated a UniqueValidator from the validation module into our ORM module. It is mapped into WireBox as UniqueValidator@cborm so you can use in your model constraints like so:
Supported Hibernate Versions
Lucee 5
Hibernate 5.4 - https://hibernate.org/orm/documentation/5.4/
You will need to update to the latest ORM Beta Extension - https://download.lucee.org/#FAD1E8CB-4F45-4184-86359145767C29DE
Adobe 2016
Hibernate 4.3 - https://hibernate.org/orm/documentation/4.3/
Adobe 2018, Adobe 2021
Hibernate 5.2 - https://hibernate.org/orm/documentation/5.2/
Basic Crud - Services
Let's do a basic example of CRUD (Create-Read-Update-Delete). We will generate a ColdBox App, connect it to a database and leverage a virtual service layer for a nice quick CRUD App.
The source code for this full example can be found in Github: https://github.com/coldbox-samples/cborm-crud-demo or in ForgeBox: https://forgebox.io/view/cborm-crud-demo
ColdBox App
Let's start by creating a ColdBox app and preparing it for usage with ORM:
Setup Environment
Season the environment file (.env) with your database credentials and make sure that database exists:
Setup ORM
Now open the Application.cfc and let's configure the ORM by adding the following in the pseudo constructor and adding two lines of code to the request start so when we reinit the APP we can also reinit the ORM.
To change the datasource name to something you like then update it here and in the .cfconfig.json file. Once done, issue a server restart and enjoy your new datasource name.
Start Server
Let's start a server and start enjoying the fruits of our labor:
If you get a Could not instantiate connection provider: org.lucee.extension.orm.hibernate.jdbc.ConnectionProviderImpl error on startup here. It means that you hit the stupid Lucee bug where on first server start the ORM is not fully deployed. Just issue a server restart to resolve this.
Create Entity - Person.cfc
Let's start by creating a Person object with a few properties, let's use CommandBox for this and our super duper coldbox create orm-entity command:
This will generate the models/Person.cfc as an ActiveEntity object and even create the unit test for it.
Setup for BDD
Since we love to promote tests at Ortus, let's configure our test harness for ORM testing. Open the /tests/Application.cfc and add the following code to setup the ORM and some functions for helping us test.
Now that we have prepared the test harness for ORM testing, let's test out our Person with a simple unit test. We don't over test here because our integration test will be more pragmatic and cover our use cases:
Basic CRUD
We will now generate a handler and do CRUD actions for this Person:
This creates the handlers/persons.cfc with the CRUD actions and a nice index action we will use to present all persons just for fun!
Please note that this also generates the integrations tests as well under /tests/specs/integration/personsTest.cfc
Inject Service
Open the handlers/persons.cfc and in the pseudo-constructor let's inject a virtual ORM service layer based on the Person entity:
The cborm module gives you the entityService:{entityName} DSL which allows you to inject virtual service layers according to entityName. With our code above we will have a personService in our variables scope injected for us.
Create
We will get an instance of a Person, populate it with data and save it. We will then return it as a json memento. The new() method will allow you to pass a struct of properties and/or relationships to populate the new Person instance with. Then just call the save() operation on the returned object.
You might be asking yourself: Where does this magic getMemento() method come from? Well, it comes from the mementifier module which inspects ORM entities and injects them with this function to allow you to produce raw state from entities. (Please see: https://forgebox.io/view/mementifier)
Read
We will get an instance according to ID and show it's memento in json. There are many ways in the ORM service and Active Entity to get objects by criteria,
In this example, we use the get() method which retrieves a single entity by identifier. Also note the default value of 0 used as well. This means that if the incoming id is null then pass a 0. The ORM services will detect the 0 and by default give you a new Person object, the call will not fail. If you want your call to fail so you can show a nice exception for invalid identifiers you can use getOrFail() instead.
Update
Now let's retrieve an entity by Id, update it and save it again!
Delete
Now let's delete an incoming entity identifier
Note that you have two choices when deleting by identifier:
Get the entity by the ID and then send it to be deleted
Use the
deleteById()and pass in the identifier
The latter allows you to bypass any entity loading, and do a pure HQL delete of the entity via it's identifier. The first option is more resource intensive as it has to do a 1+ SQL calls to load the entity and then a final SQL call to delete it.
List All
For extra credit, we will get all instances of Person and render their memento's
That's it! We are now rolling with basic CRUD cborm style!
BDD Tests
Here are the full completed BDD tests as well
Basic Crud - ActiveEntity
Let's do a basic example of CRUD (Create-Read-Update-Delete). We will generate a ColdBox App, connect it to a database and leverage ActiveEntity for a nice quick CRUD App.
The source code for this full example can be found in Github: https://github.com/coldbox-samples/cborm-crud-demo or in ForgeBox: https://forgebox.io/view/cborm-crud-demo
ColdBox App
Let's start by creating a ColdBox app and preparing it for usage with ORM:
Setup Environment
Season the environment file (.env) with your database credentials and make sure that database exists:
Setup ORM
Now open the Application.cfc and let's configure the ORM by adding the following in the pseudo constructor and adding two lines of code to the request start so when we reinit the APP we can also reinit the ORM.
To change the datasource name to something you like then update it here and in the .cfconfig.json file. Once done, issue a server restart and enjoy your new datasource name.
Start Server
Let's start a server and start enjoying the fruits of our labor:
If you get a Could not instantiate connection provider: org.lucee.extension.orm.hibernate.jdbc.ConnectionProviderImpl error on startup here. It means that you hit the stupid Lucee bug where on first server start the ORM is not fully deployed. Just issue a server restart to resolve this.
Create Entity - Person.cfc
Let's start by creating a Person object with a few properties, let's use CommandBox for this and our super duper coldbox create orm-entity command:
This will generate the models/Person.cfc as an ActiveEntity object and even create the unit test for it.
Setup for BDD
Since we love to promote tests at Ortus, let's configure our test harness for ORM testing. Open the /tests/Application.cfc and add the following code to setup the ORM and some functions for helping us test.
Now that we have prepared the test harness for ORM testing, let's test out our Person with a simple unit test. We don't over test here because our integration test will be more pragmatic and cover our use cases:
Basic CRUD
We will now generate a handler and do CRUD actions for this Person:
This creates the handlers/persons.cfc with the CRUD actions and a nice index action we will use to present all persons just for fun!
Please note that this also generates the integrations tests as well under /tests/specs/integration/personsTest.cfc
Create
We will get an instance of a Person, populate it with data and save it. We will then return it as a JSON memento. The new() method will allow you to pass a struct of properties and/or relationships to populate the new Person instance with. Then just call the save() operation on the returned object.
You might be asking yourself: Where does this magic getMemento() method come from? Well, it comes from the mementifier module wich inspects ORM entities and injects them with this function to allow you to produce raw state from entities. (Please see: https://forgebox.io/view/mementifier)
Read
We will get an instance according to ID and show it's memento in json. There are many ways in the ORM service and Active Entity to get objects by criteria,
In this example, we use the get() method which retrieves a single entity by identifier. Also note the default value of 0 used as well. This means that if the incoming id is null then pass a 0. The ORM services will detect the 0 and by default give you a new Person object, the call will not fail. If you want your call to fail so you can show a nice exception for invalid identifiers you can use getOrFail() instead.
Update
Now let's retrieve an entity by Id, update it and save it again!
Delete
Now let's delete an incoming entity identifier
Note that you have two choices when deleting by identifier:
Get the entity by the ID and then send it to be deleted
Use the
deleteById()and pass in the identifier
The latter allows you to bypass any entity loading, and do a pure HQL delete of the entity via it's identifier. The first option is more resource intensive as it has to do a 1+ SQL calls to load the entity and then a final SQL call to delete it.
List All
For extra credit, we will get all instances of Person and render their memento's
That's it! We are now rolling with basic CRUD cborm style!
BDD Tests
Here are the full completed BDD tests as well
Base ORM Service
Overview
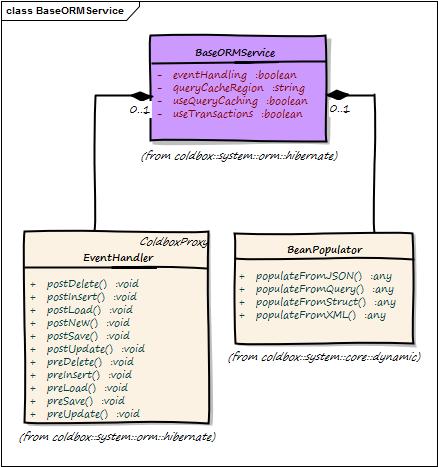
The BaseORMService is a core model CFC of the module that will provide you with a tremendous gammut of API methods to interact with ColdFusion ORM Entities.
Concept
The idea behind this support class is to provide a good base or parent service layer that can interact with ColdFusion ORM via hibernate and entities inspired by Spring's Hibernate Template support. This means that you don't need to create a service layer CFC in order to work with ORM entities.
It provides tons of methods for query executions, paging, transactions, session metadata, caching and much more. You can either use the class on its own or create more concrete service layers by inheriting from this class.
Usage
In order to get started with the base ORM service you need to know how to get access to it. You can do this via WireBox injection DSL or by the model's ID.
WireBox DSL
The module also registers a new WireBox DSL called entityservice which can produce virtual or base orm entity services that you can use to inject into your own event handlers or models.
entityservice- Inject a global ORM serviceentityservice:{entityName}- Inject a Virtual entity service according toentityName
Injection
You can also request a Base ORM Service via the registered WireBox ID which is exactly the same as the entityService DSL:
Implementation
Once you have access to the injected base ORM service, you can use it in all of its glory.
Important: Please check out the latest API Docs for the latest methods and functionality.
Once you have a reference to the base ORM service then you can use any of its methods to interact with ORM entities. The drawback about leveraging the base ORM model is that you cannot add custom functions to it or tell it to work on a specific entity for all operations. It is a simple API, but if you need more control then we can start using other approaches shown below.
Virtual Services
We also have a virtual service layer that can be mapped to specific entities and create entity driven service layers virtually. Meaning you don't have to be passing any entity names to the API methods to save you precious typing time.
Concrete Services
This is where you can create your own CFC that inherits from our Virtual or Base ORM Service model and either add or override methods. You can read more about it in our Concrete Services Section
Service Properties
There are a few properties you can instantiate a base service with or set them afterwards that affect operation. Below you can see a nice chart for them:
Property
Type
Required
Default
Description
queryCacheRegion
string
false
ORMService.defaultCache
The name of the secondary cache region to use when doing queries via this base service
useQueryCaching
boolean
false
false
To enable the caching of queries used by this base service
eventHandling
boolean
false
true
Announce interception events on new() operations and save() operations: ORMPostNew, ORMPreSave, ORMPostSave
useTransactions
boolean
false
true
Enables ColdFusion safe transactions around all operations that either save, delete or update ORM entities
defaultAsQuery
boolean
false
false
The bit that determines the default return value for list() and executeQuery() as query or array of objects
datasource
string
false
System Default
The default datasource to use for all transactions. If not set, we default it to the system datasource or the one declared in the persistent CFC.
So if I was to base off my services on top of the Base Service, I can do this:
Concrete Services
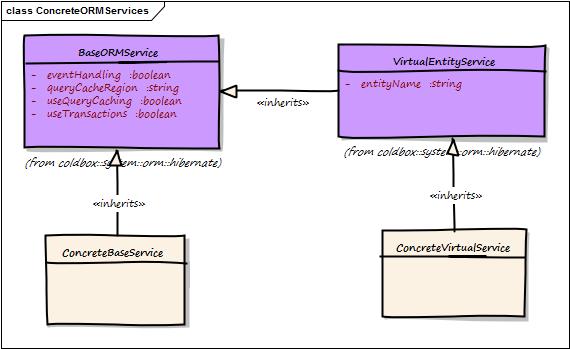
Let's say you are using the virtual services and base ORM service but you find that they do not complete your requirements, or you need some custom methods or change functionality. Then you will be building concrete services that inherit from the base or virtual entity services. This is the very purpose of these support classes as most of the time you will have custom requirements and your own style of coding.
Here is a custom AuthorService we created:
Then you can just inject your concrete service in your handlers, or other models like any other normal model object.
Service Methods
The Base ORM Service has a ton of methods to assist you with your ORM needs. We have compiled them under this section under several different categories:
Criteria Queries
Creation - Population
Counters
Deleting Entities
Entity Convenience
Finders
Getters
ORM Session
Querying
Saving
Utility
Like always, you can find the latest API Docs in the link below:
Criteria Queries
These methods allows you to tap into the Criteria Queries API so you can do fluent and functional queries with your ORM objects.
getRestrictions
Get our hibernate org.hibernate.criterion.Restrictions proxy object that will help you produce criterias.
Returns
This function returns an instance of
cborm.models.criterion.Restrictions
Examples
Adobe ColdFusion will throw an "Invalid CFML construct" for certain CBORM methods that match reserved operator names, such as .and(), .or(), and .eq(). To avoid these errors and build cross-engine compatible code, use .$and(), .$or(), and .isEq().
newCriteria
Get a brand new criteria builder object to do criteria queries with (See ORM:CriteriaBuilder)
Returns
This function returns coldbox.system.orm.hibernate.CriteriaBuilder
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
true
---
The entity name to bind the criteria query to
useQueryCaching
boolean
false
false
Do automatic query caching for queries
queryCacheRegion
string
false
criterias.{entityName}
The queryCacheRegion name property for all queries in this criteria object
datasource
string
false
The datasource to use or default it to the application or entity in use
Examples
Creation - Population
These methods allow you to create entities and populate them from external data like structures, json, xml, queries and much more.
new
Get a new entity object by entity name. You can also pass in a structure called properties that will be used to populate the new entity with or you can use optional named parameters to call setters within the new entity to have shorthand population.
Returns
This function returns the newly created entity
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
any
true
---
properties
struct
false
{}
A structure of name-value pairs to populate the new entity with
composeRelationships
boolean
false
true
Automatically attempt to compose relationships from the incoming properties memento
nullEmptyInclude
string
false
---
A list of keys to NULL when empty
nullEmptyExclude
string
false
---
A list of keys to NOT NULL when empty
ignoreEmpty
boolean
false
false
Ignore empty property values on populations
include
string
false
---
A list of keys to include in the population from the incoming properties memento
exclude
string
false
---
A list of keys to exclude in the population from the incoming properties memento
Examples
populate
Populate an entity with a structure of name-value pairs. Make sure the names of the properties match the keys in the structure.
Returns
This function returns the populated object
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
target
any
Yes
---
The entity to populate
memento
struct
Yes
---
The structure of name-value pairs to try to populate the entity with
scope
string
No
Use scope injection instead of setter injection, no need of setters, just tell us what scope to inject to
trustedSetter
Boolean
No
false
Do not check if the setter exists, just call it, great for usage with onMissingMethod() and virtual properties
include
string
No
A list of keys to ONLY include in the population
exclude
string
No
A list of keys to exclude from the population
nullEmptyInclude
string
No
A list of keys to NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
nullEmptyExclude
string
No
A list of keys to NOT NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
composeRelationships
boolean
No
true
When true, will automatically attempt to compose relationships from memento
INFO With composeRelationships=true, you can populate one-to-many, many-to-one, many-to-many, and one-to-one relationships from property values in the memento. For 'many-to-one' and 'one-to-one' relationships, the value of the property in the memento should be a single value of the primary key of the target entity to be loaded. For 'one-to-many' and 'many-to-many' relationships, the value of the property in the memento should a comma-delimited list or array of the primary keys of the target entities to be loaded.
Examples
populateFromJSON
Populate an entity with a JSON structure packet. Make sure the names of the properties match the keys in the structure.
Returns
This function returns the populated object
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
target
any
Yes
---
The entity to populate
JSONString
string
Yes
---
The JSON packet to use for population
scope
string
No
Use scope injection instead of setter injection, no need of setters, just tell us what scope to inject to
trustedSetter
Boolean
No
false
Do not check if the setter exists, just call it, great for usage with onMissingMethod() and virtual properties
include
string
No
A list of keys to ONLY include in the population
exclude
string
No
A list of keys to exclude from the population
nullEmptyInclude
string
No
A list of keys to NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
nullEmptyExclude
string
No
A list of keys to NOT NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
composeRelationships
boolean
No
true
When true, will automatically attempt to compose relationships from memento
Examples
populateFromQuery
Populate an entity with a query object. Make sure the names of the columns match the keys in the object.
Returns
This function returns the populated object
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
target
any
Yes
---
The entity to populate
qry
query
Yes
---
The query to populate with
rowNumber
numeric
false
1
The row to use to populate with.
scope
string
No
---
Use scope injection instead of setter injection, no need of setters, just tell us what scope to inject to
trustedSetter
Boolean
No
false
Do not check if the setter exists, just call it, great for usage with onMissingMethod() and virtual properties
include
string
No
---
A list of columns to ONLY include in the population
exclude
string
No
---
A list of columns to exclude from the population
nullEmptyInclude
string
No
A list of keys to NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
nullEmptyExclude
string
No
A list of keys to NOT NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
composeRelationships
boolean
No
true
When true, will automatically attempt to compose relationships from memento
Examples
populateFromXML
Populate an entity with an XML packet. Make sure the names of the elements match the keys in the structure.
Returns
This function returns the populated object
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
target
any
Yes
---
The entity to populate
xml
any
Yes
---
The xml string or xml document object to populate with
root
string
false
The xml root node to start the population with, by default it uses the XMLRoot.
scope
string
No
Use scope injection instead of setter injection, no need of setters, just tell us what scope to inject to
trustedSetter
Boolean
No
false
Do not check if the setter exists, just call it, great for usage with onMissingMethod() and virtual properties
include
string
No
A list of keys to ONLY include in the population
exclude
string
No
A list of keys to exclude from the population
nullEmptyInclude
string
No
A list of keys to NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
nullEmptyExclude
string
No
A list of keys to NOT NULL when empty, specifically for ORM population. You can also specify "*" for all fields
composeRelationships
boolean
No
true
When true, will automatically attempt to compose relationships from memento
Examples
Counters
These methods allow you to do counting on entities with or without filtering.
count
Return the count of instances in the DB for the given entity name. You can also pass an optional where statement that can filter the count. Ex: count('User','age > 40 AND name="joe"'). You can even use named or positional parameters with this method: Ex: count('User','age > ? AND name = ?',[40,"joe"])
Returns
This function returns numeric
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
where
string
No
params
any
No
strucnew()
Named or positional parameters
Examples
countWhere
Returns the count by passing name value pairs as arguments to this function. One mandatory argument is to pass the 'entityName'. The rest of the arguments are used in the where class using AND notation and parameterized. Ex: countWhere(entityName="User",age="20");
Returns
This function returns numeric
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
entityName
string
Yes
---
Examples
exists
Deleting Entities
These methods allow you to delete one or more entities in cascade style or bulk styles.
delete
Delete an entity using safe transactions. The entity argument can be a single entity or an array of entities. You can optionally flush the session also after committing.
This method will respect cascading deletes if any
Returns
This function returns void
Arguments
Key
type
Required
Default
Description
entity
any
Yes
---
flush
boolean
No
false
transactional
boolean
No
From Property
Use Transactions or not
Examples
deleteAll
Deletes all the entity records found in the database in a transaction safe matter and returns the number of records removed
This method will respect cascading deletes if any
Returns
This function returns numeric
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
The entity to purge
flush
boolean
No
false
transactional
boolean
No
From Property
Use transactions or not
Examples
deleteByID
Delete using an entity name and an incoming id, you can also flush the session if needed. The ID can be a single ID or an array of ID's to batch delete using hibernate DLM style deletes. The function also returns the number of records deleted.
No cascading will be done since the delete is done without loading the entity into session but via DLM HQL
Returns
This function returns numeric
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
The name of the entity to delte
id
any
Yes
---
A single ID or array of IDs
flush
boolean
No
false
transactional
boolean
No
From Property
Use transactions not
Examples
deleteByQuery
Delete by using an HQL query and iterating via the results. It is not performing a delete query but is a select query that should retrieve objects to remove
Returns
This function returns void
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
description
query
string
Yes
---
params
any
No
---
max
numeric
No
0
offfset
numeric
No
0
flush
boolean
No
false
transactional
boolean
No
From Property
Use transactions or not
datasource
string
false
The datasource to use or use the default datasource
Examples
deleteWhere
Deletes entities by using name value pairs as arguments to this function. One mandatory argument is to pass the 'entityName'. The rest of the arguments are used in the where class using AND notation and parameterized. Ex: deleteWhere(entityName="User",age="4",isActive=true);
Returns
This function returns numeric
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
transactional
boolean
No
From Property
Use transactions not
Examples
Entity Convenience Methods
These collection of methods will give you information about the currently loaded entity or the entity class itself.
getDirtyPropertyNames
getEntityGivenName
getEntityMetadata
This method will return to you the hibernate's metadata for a specific entity.
Returns
The Hibernate Java
ClassMetadataObject (https://docs.jboss.org/hibernate/orm/3.5/javadocs/org/hibernate/metadata/ClassMetadata.html)
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entity
any
Yes
---
The entity name or entity object
Examples
getKey
Returns the key (id field) of a given entity, either simple or composite keys.
If the key is a simple pk then it will return a string, if it is a composite key then it returns an array.
If the key cannot be identified then a blank string is returned.
Returns
This function returns any
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entity
string
Yes
---
The entity name or entity object
Examples
getKeyValue
getPropertyNames
getTableName
isDirty
refresh
Finders
Finders are convenience methods that will help you find a single entity or a collection of entities by using criterias. If you want to use primary keys, then use the getters.
findit
Finds and returns the first result for the given query or null if no entity was found. You can either use the query and params combination or send in an example entity to find.
Returns
This function returns any
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
query
string
No
---
The HQL Query to execute
params
any
No
{}
Positional or named params
timeout
numeric
No
0
ignoreCase
boolean
No
false
datasource
string
No
Examples
findOrFail
Finds and returns the first result for the given query or throws an exception if not found, this method delegates to the findIt() method
Returns
This function returns any
This function could throw an EntityNotFound exception
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
query
string
No
---
The HQL Query to execute
params
any
No
{}
Positional or named params
timeout
numeric
No
0
ignoreCase
boolean
No
false
datasource
string
No
Examples
findByExample
findWhere
Find one entity (or null if not found) according to a criteria structure ex: findWhere(entityName="Category", {category="Training"}), findWhere(entityName="Users",{age=40,retired=false});
Returns
This function returns any
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
criteria
struct
Yes
---
A structure of criteria to filter on
Examples
findAll
Find all the entities for the specified query, named or positional arguments or by an example entity
Returns
This function returns array
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
query
string
No
---
The HQL Query to execute
params
any
No
[runtime expression]
Named or positional params
offset
numeric
No
0
max
numeric
No
0
timeout
numeric
No
0
ignoreCase
boolean
No
false
datasource
string
No
asStream
boolean
No
false
Examples
findAllWhere
Find all entities according to criteria structure. Ex: findAllWhere(entityName="Category", {category="Training"}), findAllWhere(entityName="Users", {age=40,retired=true});
Returns
This function returns array
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
criteria
struct
Yes
---
A structure of criteria to filter on
sortOrder
string
false
---
The sort ordering
ignoreCase
boolean
false
false
timeout
numeric
false
0
asStream
boolean
false
false
Examples
Getters
Here is a collection of useful getter methods for entities by primary identifiers. Getters mostly deal with retrieving entities by primary keys instead of finders which rely on criteria operations. You can use the get() for a single entity, getOrFail() for throwing exceptions if an entity is not found and getAll() for multiple entities.
get
Get an entity using a primary key, if the id is not found this method returns null. You can also pass an id = 0 and the service will return to you a new entity.
No casting is necessary on the Id value type as we do this automatically for you.
Returns
This function returns any
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
id
any
Yes
---
returnNew
boolean
false
true
If id is 0 or empty and this is true, then a new entity is returned.
Examples
getOrFail
Get an entity using a primary key, if the id is not found this method throws an EntityNotFound Exception
No casting is necessary on the Id value type as we do this automatically for you.
Returns
This function returns any
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
id
any
Yes
---
Examples
getAll
Retrieve all the instances from the passed in entity name using the id argument if specified. The id can be a list of IDs or an array of IDs or none to retrieve all. If the id is not found or returns null the array position will have an empty string in it in the specified order
You can use the readOnly argument to give you the entities as read only entities.
You can use the properties argument so this method can return to you array of structs instead of array of objects. The property list must include the as alias if not you will get positional keys.
Example Positional: properties="catID,category Example Aliases: properties="catID as id, category as category, role as role"
You can use the asStream boolean argument to get either an array of objects or a Java stream via cbStreams.
No casting is necessary on the Id value type as we do this automatically for you.
Returns
This function returns array of entities found
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
true
---
id
any
false
---
sortOrder
string
false
---
The sort orering of the array
readOnly
boolean
false
false
properties
string
false
If passed, you can retrieve an array of properties of the entity instead of the entire entity. Make sure you add aliases to the properties: Ex: 'catId as id'
Examples
ORM Session
clear
Clear the session removes all the entities that are loaded or created in the session. This clears the first level cache and removes the objects that are not yet saved to the database.
Returns
This function returns the base service reference (
this)
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
datasource
string
false
---
The default or specific datasource use
Examples
evict
evictCollection
Evict all the collection or association data for a given entity name and collection name from the secondary cache ONLY, not the hibernate session.
Evict an entity name with or without an ID from the secondary cache ONLY, not the hibernate session
Returns
This function returns void
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
The entity name to evict or use in the eviction process
relationName
string
false
The name of the relation in the entity to evict
id
any
false
The id to use for eviction according to entity name or relation name
Examples
evictQueries
getSessionStatistics
isSessionDirty
merge
sessionContains
Querying
These methods are used for doing a-la-carte querying of entities with extra pizzaz!
executeQuery
Allows the execution of Custom HQL queries with binding, pagination, and many options. Underlying mechanism is ORMExecuteQuery. The params filtering can be using named or positional.
Returns
This function returns multiple formats:
array of objects
array of structs
query
cbStream
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
query
string
Yes
---
The valid HQL to process
params
array or struct
No
Positional or named parameters
offset
numeric
No
0
Pagination offset
max
numeric
No
0
Max records to return
timeout
numeric
No
0
Query timeout
asQuery
boolean
No
false
Return query or array of objects
unique
boolean
No
false
Return a unique result
datasource
string
No
---
Use a specific or default datasource
Examples
list
List all of the instances of the passed in entity class name with or without any filtering of properties, no HQL needed.
You can pass in several optional arguments like a struct of filtering criteria, a sortOrder string, offset, max, ignorecase, and timeout. Caching for the list is based on the useQueryCaching class property and the cachename property is based on the queryCacheRegion class property.
Returns
This function returns array if asQuery = false
This function returns a query if asQuery = true
This function returns a stream if asStream = true
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
Yes
---
The entity to list
criteria
struct
No
A struct of filtering criteria for the listing
sortOrder
string
No
The sorting order of the listing
offset
numeric
No
0
Pagination offset
max
numeric
No
0
Max records to return
timeout
numeric
No
0
Query timeout
ignoreCase
boolean
No
false
Case insensitive or case sensitive searches, we default to case sensitive filtering.
asQuery
boolean
No
false
Return query or array of objects
Examples
Saving Entities
save
Save an entity using hibernate transactions or not. You can optionally flush the session also.
Returns
This function returns void
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entity
any
Yes
---
The entity to save
forceInsert
boolean
No
false
Insert as new record whether it already exists or not
flush
boolean
No
false
Do a flush after saving the entity, false by default since we use transactions
transactional
boolean
No
true
Wrap the save in a ColdFusion transaction
Examples
saveAll
Saves an array of passed entities in specified order and transaction safe
Returns
This function returns void
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entities
array
Yes
---
The array of entities to persist
forceInsert
boolean
No
false
flush
boolean
No
false
transactional
boolean
No
true
Use ColdFusion transactions or not
Examples
Utility Methods
autoCast
This method allows you to cast any value to the appropriate type in Java for the property passed in. The entity argument can be the entity name or an entity object.
Returns
This function returns the value casted to the right Java type
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entity
string
Yes
The entity name or entity object
propertyName
string
Yes
The property name
value
any
Yes
The property value
Examples
createService
Create a virtual service for a specific entity. Basically a new service layer that inherits from the BaseORMService object but no need to pass in entity names, they are bound to the entity name passed here.
Returns
This function returns VirtualEntityService
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
entityName
string
Yes
---
useQueryCaching
boolean
No
Same as BaseService
queryCacheRegion
string
No
Same as BaseService
eventHandling
boolean
No
true
useTransactions
boolean
No
true
defaultAsQuery
boolean
No
true
datasource
string
No
The default app datasource
Examples
idCast
This method allows you to cast the identifier value to the appropriate type in Java. The entity argument can be the entity name or an entity object. Please note that this is ONLY used for identifier casting not for any property!
Returns
This function returns the value casted to the right Java type
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
entity
string
Yes
The entity name or entity object
id
any
Yes
The value to cast
Examples
when
This method gives you the ability to fluently create chains of executions by evaluating the incoming target as a boolean. If true it will execute the success closure, else the failure closure if passed.
Returns
The ORM Service so you can do concatenated calls
Arguments
Key
Type
Required
Default
Description
target
boolean
Yes
A boolean evaluator
success
closure
Yes
The closure to execute if the target is true
failure
closure
No
The closure to execute if the target is false
Examples
Dynamic Finders- Counters
The ORM module supports the concept of dynamic finders and counters for ColdFusion ORM entities. A dynamic finder/counter looks like a real method but it is a virtual method that is intercepted by via onMissingMethod. This is a great way for you to do finders and counters using a programmatic and visual representation of what HQL to run.
This feature works on the Base ORM Service, Virtual Entity Services and also Active Entity services. The most semantic and clear representations occur in the Virtual Entity Service and Active Entity as you don't have to pass an entity name around.
Automatic Casting
Another important aspect of the dynamic finders is that we will AUTO CAST all the values for you. So you don't have to mess with the right Java type, we will do it for you.
Streams
We have also enabled the ability to return a stream of objects if you are using the findAll semantics via cbStreams.
Method Signatures
We have three types of dynamic finders and counters:
findBy: Find ONE entity according to method signature, if more than one record is found an exception is thrownfindAllBy: Find ALL entities according to method signaturecountBy: Give you a count of entities according to method signature
Let's say you have the following entity:
Then we could do the following:
You can also use the virtual entity service instead of active entity.
If you just use a vanilla Base ORM Service, then the first argument must be the entityName:
Method Expressions
A method expression is made up of the prefixes: findBy, findAllBy, countBy followed by the expression that combines a query upon one or more properties:
If a conditional keyword is not passed, we assume you want equality. Remember that!
IMPORTANT: The ? means that you can concatenate the same pattern over and over again.
Conditionals
The available conditionals in ColdBox are:
LessThanEquals- Less than or equal to passed valueLessThan- Less than to passed valueGreaterThanEquals- Greater than or equal to passed valueGreaterThan- Greater than to passed valueLike- Equivalent to the SQL like expressionNotEqual- Not equal to the passed valueisNull- The property must be nullisNotNull- The property must not be nullNotBetween- The property value must not be between two valuesBetween- The property value must be between two valuesNotInList- The property value must not be in the passed in simple list or arrayinList- The property value must be in the passed in simple list or array
Operators
The only valid operators are:
AndOr
Query Options
If you pass a structure as the last argument to your dynamic finder/counter call, we will consider that by convention to be your query options.
The valid query options are:
ignorecase: Ignores the case of sort order when you set it to true.maxResults: Specifies the maximum number of objects to be retrieved.offset: Specifies the start index of the resultset from where it has to start the retrieval.cacheable: Whether the result of this query is to be cached in the secondary cache. Default is false.cachename: Name of the cache in secondary cache.timeout: Specifies the timeout value (in seconds) for the querydatasource: The datasource to use, it defaults to the applicationsortBy: The HQL to sort the query byautoCast: No more casting, let us do auto casting for youasStream: Want a stream back instead of the results, no problem!
Here is a more descriptive key set with the types and defaults
Automatic Java Types
Most of the Hibernate extensions like criteria builders and even some dynamic finders and counters will have to rely on the underlying Java types in order to work. You do this in ColdFusion by using the javaCast() function available to you. So if you are using a primary key that is an Integer you might have to do the following in order to match your variable to the underlying Java type:
If you do not type it, then ColdFusion assumes it is a string and passes a string to Hibernate which will throw an exception as it is supposed to be an integer.
Auto Types
We have created two methods available to you in the base orm service, virtual service, criteria builders, active entity, etc to help you with these translations by automatically casting the values for you:
nullValue()
nullValue()Produce a null value that can be used anywhere you like!
autoCast( entity, propertyName, value )
autoCast( entity, propertyName, value )This method allows you to cast any value to the appropriate type in Java for the property passed in. The entity argument can be the entity name or an entity object.
idCast( entity, id )
idCast( entity, id )This method allows you to cast the identifier value to the appropriate type in Java. The entity argument can be the entity name or an entity object.
Example
So instead of casting it manually you can just let us do the work:
Virtual Services
Overview
The virtual entity service is another support class that can help you create virtual service layers that are bounded to a specific ORM entity for convenience. This class inherits from our Base ORM Service and allows you to do everything the base class provides, except you do not need to specify to which entityName or entity you are working with.
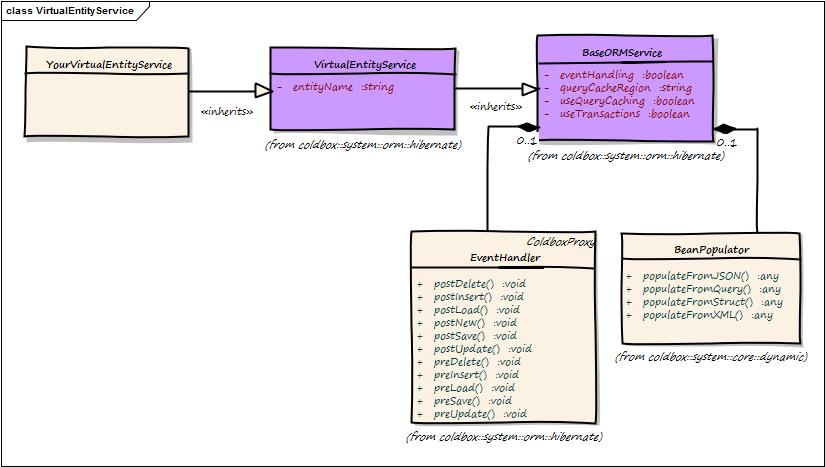
You can also use this class as a base class and template out its methods to more concrete usages. The idea behind this virtual entity service layer is to allow you to have a very nice abstraction to all the CF ORM capabilities (hibernate) and promote best practices.
Tip: Please remember that you can use ANY method found in the Base ORM Service except that you will not pass an argument of entityName anymore as you have now been bounded to that specific entity.
Injection Virtual Services
The WireBox injection DSL has an injection namespace called entityService that can be used to wire in a Virtual Entity Service bound to ANY entity in your application. You will use this DSL in conjunction with the name of the entity to manage it.
Inject Content
Description
entityService:{entity}
A virtual service based on the {entity}
Requesting Virtual Services
You can also request a virtual service via the getInstance() method in your handlers or view a wirebox.getInstance() call:
Mapping Virtual Services
You can also leverage the WireBox Binder to map your virtual services so you can abstract the object's constructions or add constructor arguments to their definition and have full control:
Now you can just use it via the UserService alias:
Service Properties
There are a few properties you can instantiate the virtual service with or set them afterwards that affect operation. Below you can see a nice chart for them:
Property
Type
Required
Default
Description
entityName
string
true
The entity name to bind the virtual service with.
queryCacheRegion
string
false
#entityName#.defaultVSCache
The name of the secondary cache region to use when doing queries via this service
useQueryCaching
boolean
false
false
To enable the caching of queries used by this service
eventHandling
boolean
false
true
Announce interception events on new() operations and save() operations: ORMPostNew, ORMPreSave, ORMPostSave
useTransactions
boolean
false
true
Enables ColdFusion safe transactions around all operations that either save, delete or update ORM entities
defaultAsQuery
boolean
false
false
The bit that determines the default return value for list(), executeQuery() as query or array of objects
datasource
string
false
System Default
The default datasource to use for all transactions. If not set, we default it to the system datasource or the one declared in the persistent CFC.
To create a virtual service you can do this:
Concrete Virtual Services
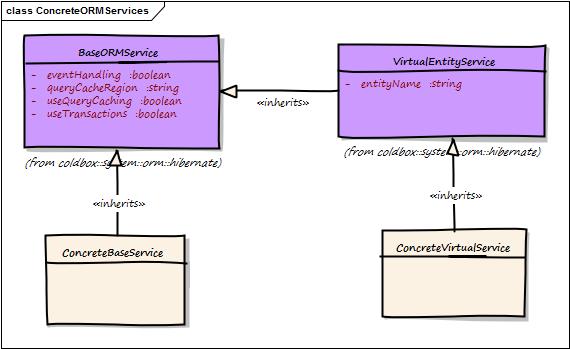
Let's say you are using the virtual service but you find that they do not complete your requirements, or you need some custom methods or change functionality. Then you will be building concrete services that inherit from the virtual entity service. This is the very purpose of these support classes as most of the time you will have custom requirements and your own style of coding. You will do this in two steps:
Inherit from
cborm.models.VirtualEntityServiceCall the
super.init()constructor with the entity to root the service and any other options
Below is a sample service layer:
Active Record
Active Entity Overview

This class allows you to implement the Active Record pattern in your ORM entities by inheriting from our Active Entity class. This will make your ORM entities get all the functionality of our Virtual and Base ORM services so you can do finds, searches, listings, counts, execute queries, transaction safe deletes, saves, updates, criteria building, and even validation right from within your ORM Entity.
The idea behind the Active Entity is to allow you to have a very nice abstraction to all the ColdFusion ORM capabilities (hibernate) and all of our ORM extensions like our ColdBox Criteria Builder. With Active Entity you will be able to:
Find entities using a variety of filters and conditions
ORM paging
Specify order, searches, criterias and grouping of orm listing and searches
Use DLM style hibernate operations for multiple entity deletion, saving, and updating
Check for existence of records
Check for counts using criterias
Use our extensive ColdBox Criteria Builder to build Object Oriented HQL queries
Validate your entity using cbValidation
Configuration
To work with Active Entity you must do a few things to tell ColdBox and Hibernate you want to use Active Entity:
Enable the ORM in your
Application.cfcwith event handling turned on, manage session and flush at request end as false. This will allow Hibernate to talk to the cborm event handling objects.Enable the orm configuration structure in your ColdBox configuration to allow for ColdBox to do entity injections via WireBox.
Application.cfc
The following are vanilla configurations for enabling the ORM in ColdFusion:
Module Settings
Open your config/ColdBox.cfc and either un-comment or add the following settings:
This enables WireBox dependency injection, which we need for ActiveEntity to work with validation and other features. Check out our installation section if you need a refresher.
Building Entities
Once your configuration is done we can now focus on building out your Active Entities. You will do so by creating your entities like normal ORM objects but with two additions:
They will inherit from our base class:
cborm.models.ActiveEntityIf you have a constructor then it must delegate to the super class via
super.init()
Please remember that your entities inherit all the functionality of the base and virtual services. Except no entity names or datasources are passed around.
Constructor Properties
There are a few properties you can instantiate the ActiveEntity with or set them afterwards that affect operation. Below you can see a nice chart for them:
Property
Type
Required
Default
Description
queryCacheRegion
string
false
#entityName#.activeEntityCache
The name of the secondary cache region to use when doing queries via this entity
useQueryCaching
boolean
false
false
To enable the caching of queries used by this entity
eventHandling
boolean
false
true
Announce interception events on new() operations and save() operations: ORMPostNew, ORMPreSave, ORMPostSave
useTransactions
boolean
false
true
Enables ColdFusion safe transactions around all operations that either save, delete or update ORM entities
defaultAsQuery
boolean
false
false
The bit that determines the default return value for list(), executeQuery() as query or array of objects
Here is a nice example of calling the super.init() class with some of these constructor properties.
Usage
Now that you have created your entities, how do we use them? Well, you will be using them from your handlers or other services by leveraging WireBox's getInstance() method. You can use entityNew() as well, but if you do, you will loose any initial dependency injection within the entity. This is a ColdFusion limitation where we can't listen for new entity constructions. If you want to leverage DI, as best practice retrieve everything from WireBox.
Once you have an instance of the entity, then you can use it to satisfy your requirements with the entire gamut of functions available from the base services.
Tip: You can also check out our Basic CRUD guide for an initial overview of the usage.
Validation
Validation Functions
Our active entity object will also give you access to our validation engine (cbValidation) by giving your ORM entities the following functions:
Declaring Constraints
This makes it really easy for you to validate your ORM entities in two easy steps:
1) Add your validation constraints to the entity
2) Call the validation methods
Let's see the entity code so you can see the constraints:
Validating Constraints
Now let's check out the handlers to see how to validate the entity via the isValid() function:
Please remember that the isValid() function has several arguments you can use to fine tune the validation:
fields
constraints
locale
excludeFields
Displaying Errors
You can refer back to the cbValidation docs for displaying errors:
Here are the most common methods for retreving the errors from the Result object via the getValidationResults() method:
getResultMetadata()getFieldErrors( [field] )getAllErrors( [field] )getAllErrorsAsJSON( [field] )getAllErrorsAsStruct( [field] )getErrorCount( [field] )hasErrors( [field] )getErrors()
The API Docs in the module (once installed) will give you the latest information about these methods and arguments.
Unique Property Validation
We have also integrated a UniqueValidator from the validation module into our ORM module. It is mapped into WireBox as UniqueValidator@cborm so you can use it in your model constraints like so: